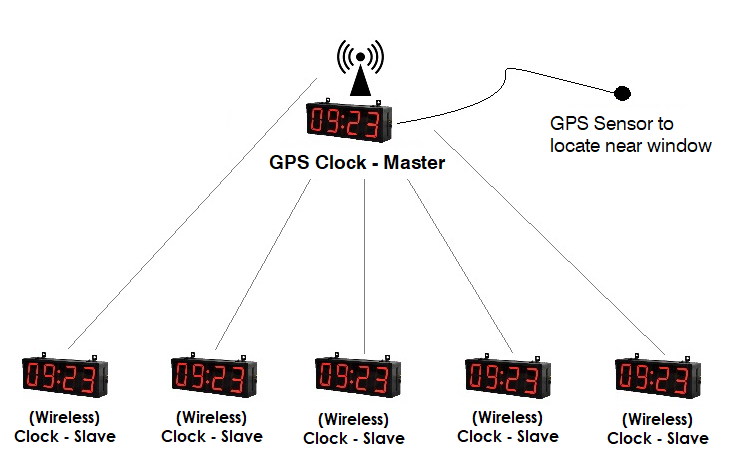


A master clock systems is a centralized timekeeping solution used in various settings, such as hospitals, schools, factories, and large office buildings. It ensures that all clocks within a facility are synchronized to the same accurate time, enhancing coordination and efficiency across operations.

A master clock serves as the primary time source, distributing time signals to all connected slave clocks throughout the facility.

Ensures that all clocks are synchronized to the same time, minimizing discrepancies and improving time management.

Modern master clock systems can connect to various types of clocks, including analog, digital, and networked clocks, accommodating different environments and preferences.

Many systems come with user-friendly interfaces, allowing for easy adjustments and monitoring of time settings from a central location..

Master clock systems can integrate with other technology, such as access control systems, alarm systems, and scheduling software, providing a comprehensive time management solution.
Initial setup and installation of a master clock system can be costly, particularly in large facilities.
Regular maintenance and updates are necessary to ensure continued accuracy and functionality.
Integrating with existing clock systems may pose challenges, especially in older infrastructures.
| Protocol | Description | Features | Use Cases |
| NTP (Network Time Protocol) | A widely used protocol designed to synchronize the clocks of computers over a network. |
| Commonly used in IT networks, data centers, and enterprise environments. |
| PTP (Precision Time Protocol) | A protocol designed for high-precision time synchronization, particularly in local area networks (LANs). |
| Used in industries like broadcasting, manufacturing, and power generation. |
| IRIG (Inter-Range Instrumentation Group) | A time code standard used primarily in military and aerospace applications. |
| Common in scientific research, aerospace, and military systems. |
| GPS (Global Positioning System) | A satellite-based navigation system that provides accurate time and location data. |
| Used in aviation, maritime navigation, and any application requiring precise timing. |
| IEEE 1588 | The standard that defines PTP for clock synchronization in networked systems. |
| Widely adopted in industrial automation, telecommunications, and smart grid applications. |
| Synchronous Ethernet (SyncE) | A synchronization method that uses Ethernet technology to provide precise timing. |
| Used in telecommunications networks, particularly for backhaul and transport networks. |
| Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) | A simplified version of NTP, designed for environments where high precision is not critical. |
| Suitable for consumer devices and less critical applications. |
Al Shareef Telecom: Different synchronization protocols serve various needs, from high-precision applications in industrial settings to simpler implementations in consumer electronics. Choosing the right protocol depends on the specific requirements for accuracy, network infrastructure, and the type of application involved.

