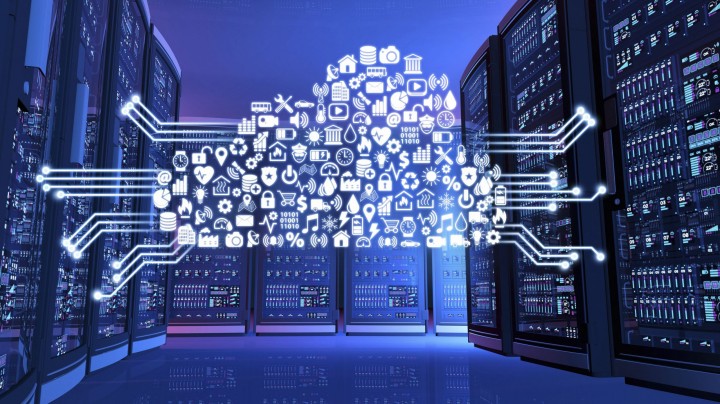



Design and implementation of ELV systems for data centers and IT rooms, including power management, cooling systems, and security systems, ensuring high availability and reliability.
Data centers and IT rooms are essential components of modern technology infrastructure, housing the critical systems and hardware that store, process, and manage data for organizations. Below is an explanation of their characteristics, designs, functions, and differences between the two.
A data center is a large facility that houses many computer servers and related components such as storage systems, networking hardware, and data communication systems. These facilities are designed to handle high volumes of data processing, storage, and transmission.
Data centers are designed to scale up easily with added hardware and infrastructure, accommodating increased loads and storage requirements.

They incorporate multiple backup systems (power supplies, cooling systems, network connections) to ensure continuous operation even if primary systems fail.

Data centers implement stringent physical and cyber security measures, including access controls, surveillance systems, firewalls, and encryption technologies.
Advanced air conditioning and cooling systems are essential to maintain optimal operating temperatures for servers and other hardware.

Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS), backup generators, and power distribution units ensure uninterrupted power and protection against outages.

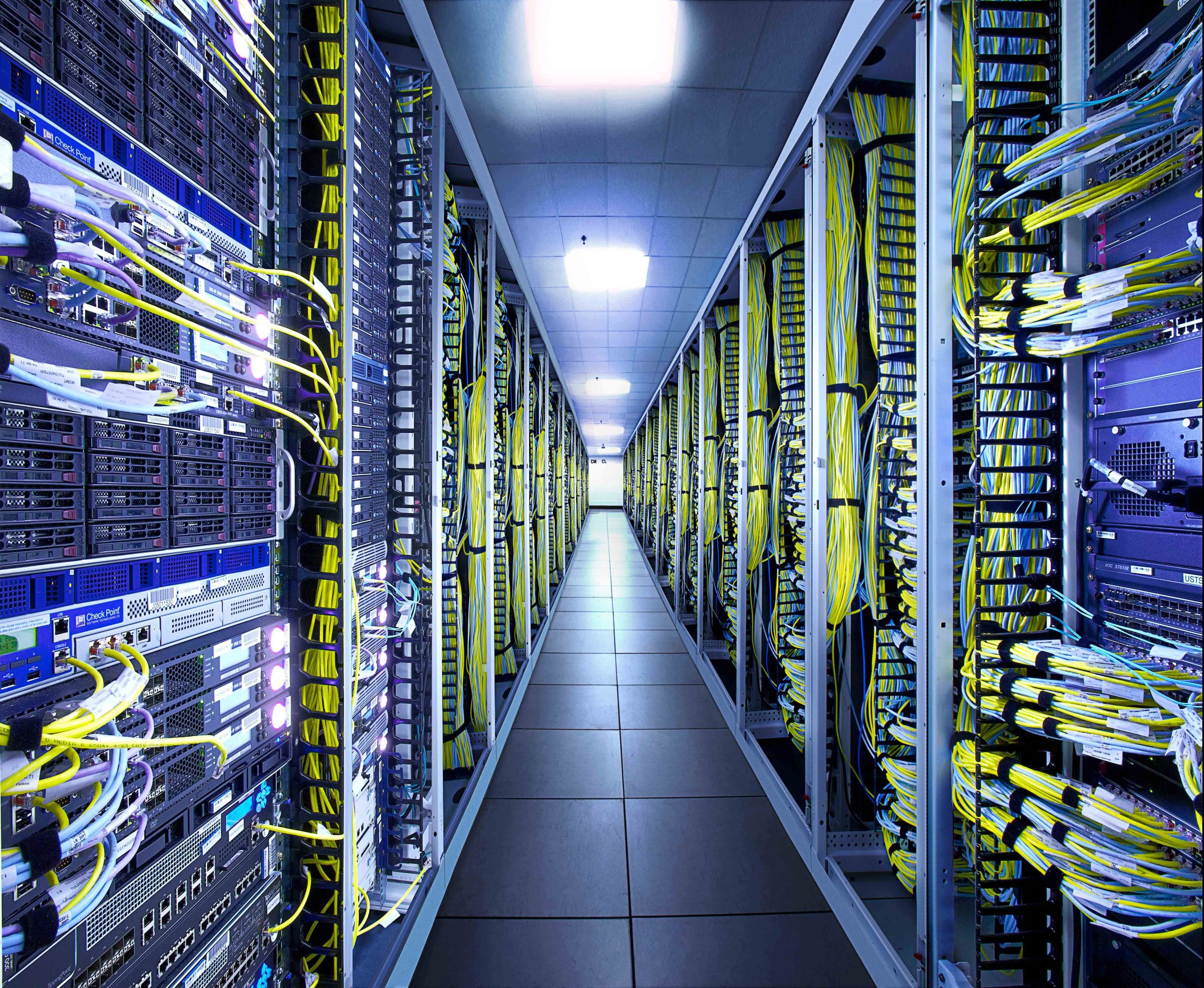
Data centers often contain extensive networking equipment to support high-speed data transfer both internally and externally.
IT rooms, often referred to as server rooms or computer rooms, are smaller facilities typically located within an organization that house a limited amount of IT hardware. They can include servers, networking equipment, and storage systems but are usually less expansive than data centers.
IT rooms are generally smaller than data centers, often designed to handle the specific needs of a single organization or department.
While organizations may incorporate some redundancy for critical systems, IT rooms typically have less comprehensive plans than large data centers.
Setting up an IT room often requires less capital than establishing a full-scale data center, making it a feasible option for smaller organizations.
While IT rooms still require security measures, they may not have the same level of physical security as dedicated data centers.
| Feature | Data Centers | IT Rooms |
| Size | Large facilities with multiple racks | Smaller, often a single room or area |
| Scalability | Highly scalable to accommodate growth | Limited scalability |
| Redundancy | Multiple layers of redundancy | Basic or limited redundancy |
| Security | Advanced security measures | Basic security measures |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost of setup |
| Functionality | Comprehensive data processing, storage, and hosting | Localized application hosting and support |
Both data centers and IT rooms play crucial roles in an organization’s IT infrastructure. The choice between establishing a data center or an IT room often depends on the organization’s size, budget, workload requirements, and long-term growth plans. Data centers provide extensive capabilities for large-scale operations, while IT rooms are suitable for smaller, local needs. Understanding their features, functions, and differences is vital for effective IT planning and management.
